Key Takeaways:
- Robot palletizers often deliver the fastest ROI among end-of-line automation equipment by eliminating manual labor and reducing ergonomic injury risks.
- Real-time data synchronization through integrated software improves operational efficiency and enables quicker decision-making across packaging lines.
- Predictive maintenance with IoT sensors tracking temperature, vibration, and humidity extends equipment lifespan and reduces unplanned downtime.
- Companies like BMW and Toyota use AI for motor current monitoring to predict equipment failures before they occur in integrated systems.
- Multi-robot coordination platforms are emerging as solutions for managing complex packaging line synchronization and maintaining precise machine timing.
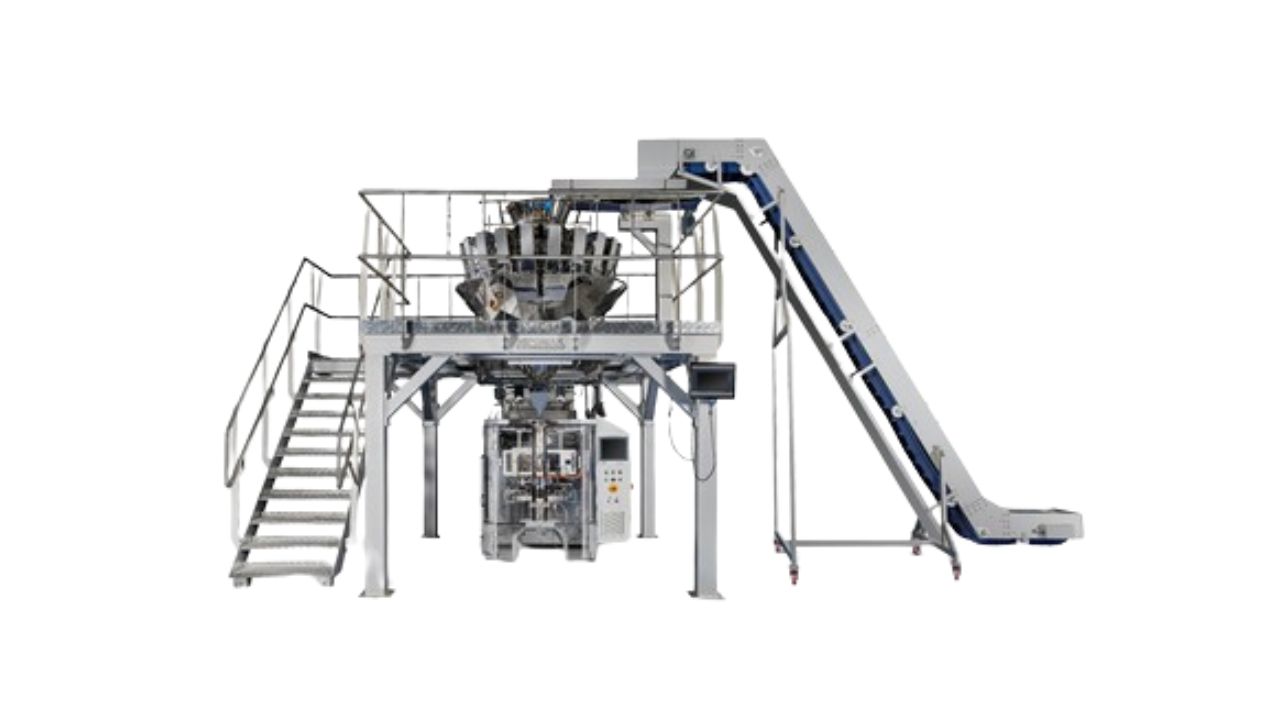
Integrated packaging lines connect independent machines into coordinated systems operating as single units. This integration spans weighing, filling, vffs packaging machine operations, inspection, case packing, and palletizing. Complete integration eliminates manual material handling, reduces labor requirements, and increases throughput. ROI analysis quantifies these benefits against capital investment, revealing payback timelines and long-term financial impact.
What does complete packaging line integration mean from weighing to palletizing?
Complete integration connects all packaging equipment through unified controls, synchronized timing, and continuous material flow. It transforms individual machines into a coordinated production system where each component responds to upstream and downstream conditions.
How is an integrated packaging line structured across weighing, filling, packaging, and palletizing?
The line begins with weighing and filling equipment that doses product into containers. Primary packaging machines—VFFS, flow wrappers, or pouch fillers—seal products into retail packages. End-of-line automation includes case packing, palletizing, and stretch wrapping as the final stages of a complete integrated system. Conveyors connect each stage and buffer speed variations. Material flows continuously from raw product to finished pallets without manual intervention.
How does control integration unify all machines into a single coordinated system?
Synchronizing different control systems and software platforms is critical for efficient operations in integrated packaging lines. A master controller communicates with individual machine PLCs using standard industrial protocols. Cutting-edge software applications enhance inter-system connectivity by enabling real-time data exchange, minimizing delays, and reducing errors. Integration software is user-friendly and customizable to meet specific business needs.
How does a fully connected line differ from standalone, non-synchronized equipment?
Standalone equipment operates independently without awareness of upstream or downstream conditions. System integration services ensure every component operates in flawless unison, enhancing efficiency and productivity while minimizing downtime and costs, which standalone equipment cannot achieve. Connected lines automatically adjust speeds, accumulate product during delays, and restart synchronously after stoppages.
Why does complete line integration matter for operational and financial performance?
Integration delivers measurable improvements in throughput, labor efficiency, quality consistency, and operational visibility. These improvements translate directly into financial returns through increased output and reduced costs.
How does integration increase line throughput, reduce stoppages, and improve OEE?
Real-time data synchronization is critical for coordinating equipment performance and preventing stoppages across integrated packaging lines. Integrated systems eliminate bottlenecks by matching speeds across equipment zones. Automatic accumulation buffers temporary slowdowns without stopping upstream machines. OEE improvements of 10 to 25 percentage points are common after integration.
How does integration reduce labor dependency, material handling, and ergonomic risk?
Automated material flow eliminates manual transfer between machines. Robot palletizers often deliver the fastest ROI among end-of-line automation equipment by eliminating manual palletizing labor and reducing ergonomic injury risks. Single-operator line supervision replaces multi-person material handling crews. Labor reduction typically ranges from 40% to 70% depending on line length and previous automation level.
How does integration improve traceability, quality verification, and regulatory compliance?
Integrated control systems record production data automatically. Lot tracking connects raw materials to finished pallets without manual documentation. In-line inspection devices—checkweighers, metal detectors, vision systems—reject defects automatically and log all rejections. Electronic batch records eliminate transcription errors and incomplete documentation that occur with manual systems.
What equipment modules are typically included in a weighing-to-palletizing system?
Integrated lines comprise five functional zones: dosing, primary packaging, secondary packaging, inspection, and palletizing. Equipment selection within each zone depends on product characteristics, speed requirements, and format variety.
How do weighers, volumetric fillers, or auger fillers anchor the start of the line?
Dosing equipment controls the product quantity entering each package. Weighers provide the highest accuracy for value-based products. Volumetric fillers deliver faster speeds for consistent-density materials. Multi-head combination weighers optimize speed and accuracy for snack foods and dry products. Dosing accuracy impacts product giveaway costs and regulatory compliance. Integration connects filler speed to downstream capacity, preventing overproduction and product accumulation.
How do primary packaging machines (VFFS, flow wrappers, premade pouch fillers) shape the cycle rate?
Primary packaging equipment determines maximum line speed because it creates the individual sellable unit. Quick-change tooling systems are becoming standard in modern packaging equipment, enabling faster format transitions that protect cycle rate. Digital calibration presets and recipe-based settings enable faster transitions between products, reducing the impact of changeovers on overall cycle rate.
How do case packers, bundlers, and cartoners organize finished packs for shipment?
Secondary packaging consolidates individual packages into shippable units. Case packers load products into corrugated cases using robotic pick-and-place or drop-packing mechanisms. Secondary packaging typically operates more slowly than primary packaging, requiring accumulation between stages. Integration prevents upstream equipment from overwhelming case packers during temporary slowdowns.
How do palletizers, stretch wrappers, and conveyors finalize the end-of-line flow?
Palletizers stack cases into stable pallet loads using robotic arms or layer-forming systems. Stretch wrappers apply film to secure loads for shipping. Integration ensures smooth handoffs between each device and synchronizes pallet presentation. Conveyors provide buffer storage during pallet changeovers and stretch-wrap cycles.
How does system layout and engineering design affect full-line performance?
Physical layout determines material flow efficiency, operator access, maintenance accessibility, and future expansion capability. Poor layout creates unnecessary conveyance, difficult changeovers, and constrained throughput.
How does line layout influence material flow, operator access, and equipment spacing?
Linear layouts minimize conveyance length and simplify material flow but require long floor spans. L-shaped and U-shaped configurations fit compact spaces and position operators near multiple machines. Equipment spacing must accommodate maintenance access, forklift traffic, and safety clearances. Layout decisions balance throughput optimization against available floor area and building constraints.
How do accumulation tables and conveyors buffer upstream and downstream variations?
Accumulation conveyors store product during temporary speed mismatches. Dynamic accumulation uses sensor-controlled zones that start and stop independently. Proper accumulation prevents line stalls when downstream equipment experiences brief delays. Buffer sizing depends on downstream recovery time and upstream production rate.
How do sanitation zones, airflow, and environmental conditions affect integration planning?
Food-grade facilities require wash-down capability, sanitary design, and segregated processing zones. Allergen controls demand physical separation between product streams. Temperature and humidity requirements influence equipment selection and facility design. Integration planning must address these requirements during initial design to avoid costly retrofits.
How does control architecture determine integration quality and line coordination?
Controls architecture establishes communication protocols, data structures, and functional hierarchy. Well-designed architecture enables seamless coordination and future equipment additions.
How do PLC platforms, HMIs, and communication protocols synchronize machine timing?
A master PLC coordinates line functions and communicates with individual machine controllers. Multi-robot coordination platforms are emerging as solutions for managing complex packaging line synchronization and maintaining precise machine timing across integrated systems. The HMI provides a unified visualization of line status, alarms, and production metrics. Standardized communication enables equipment from different manufacturers to operate cohesively.
How do smart sensors, feedback loops, and reject logic maintain continuous flow?
Sensors detect product presence, position, and orientation at critical transfer points. Feedback loops adjust equipment speeds based on accumulation levels and downstream capacity. Photo eyes trigger reject mechanisms when inspection systems identify defects. Smart sensors enable predictive maintenance by monitoring vibration, temperature, and electrical current.
How does data connectivity enable performance monitoring, alarms, and predictive maintenance?
IoT enables real-time monitoring and failure prediction across packaging equipment. Companies like BMW and Toyota use AI for motor current monitoring to predict equipment failures before they occur. Connected systems transmit performance data to enterprise software for OEE tracking and production reporting. Cloud connectivity enables remote diagnostics and vendor support without site visits.
Which cost factors belong in a complete packaging line ROI calculation?
ROI calculations must capture all relevant costs and benefits. Comprehensive analysis includes capital costs, operating costs, and financial benefits.
How should you model equipment cost, installation cost, and integration engineering cost?
Equipment cost includes machines, controls, conveyors, and safety systems. Installation cost covers rigging, electrical, compressed air, and structural modifications. Integration engineering encompasses controls programming, system testing, and commissioning. Total capital investment typically equals 1.2 to 1.5 times base equipment cost after all installation expenses.
How do labor, overtime, and staffing shifts influence the ROI calculation?
Labor savings represent the largest financial benefit in most integration projects. Calculate current labor hours per shift and multiply by loaded labor rates. Compare current staffing to projected requirements after integration. Multi-shift operations multiply labor savings proportionally. Consider hiring freezes or natural attrition rather than layoffs when modeling labor reductions.
How do scrap reduction, product giveaway control, and quality improvements affect financial impact?
Improved accuracy reduces product giveaway by delivering target weights without excess overfill. Reduced manual handling decreases package damage and rejected products. Calculate scrap value as (current reject rate - future reject rate) × production volume × product cost. Quality improvements also reduce raw material waste and regulatory risk.
How do energy use, spare parts, and long-term maintenance shape lifecycle cost?
Electrical sensors continuously track power and current levels to optimize energy usage, reduce operational costs, and prevent equipment failures. Modern equipment typically consumes 10% to 30% less energy than older machines. Predictive maintenance avoids unnecessary maintenance tasks by addressing needs based on actual equipment condition rather than fixed schedules, reducing lifecycle maintenance costs. Lifecycle analysis should span 7 to 10 years to capture long-term cost patterns.
How should you gather baseline performance data before building the ROI model?
Accurate baseline data ensures ROI models reflect actual conditions rather than assumptions. Systematic data collection establishes credible performance benchmarks.
How do you collect current throughput, downtime, and OEE metrics from existing equipment?
Track production output hourly for two weeks to establish average throughput. Record all downtime events by category: changeovers, breakdowns, material shortages, and quality issues. Calculate OEE as (availability × performance × quality). Baseline data reveals improvement opportunities and validates vendor performance claims.
How do you quantify labor utilization, manual handling, and changeover losses?
Observe and time all manual material handling activities. Count the operators required per shift and document their specific tasks. Viking Masek reports achieving changeover in under 5 minutes on rotary pouch fill and seal machines, establishing a concrete benchmark for measuring changeover losses in baseline performance data. Document overtime hours driven by production demands. Labor data quantifies the financial benefit of automation.
How do you document reject rates, quality issues, and scrap levels?
Weigh or count rejected product daily by rejection reason. Calculate the reject rate as (rejected units ÷ total units produced) × 100. Track product giveaway by comparing actual package weights to target specifications. Quality data reveals opportunities for inspection systems and process control improvements.
What are the main steps to calculating ROI for a fully integrated packaging line?
ROI calculation follows a structured process that defines requirements, models performance, quantifies benefits, and calculates financial returns.
Step 1 — How do you define capacity, speed targets, and system constraints?
Establish required production capacity in units per hour or cases per shift. Define product mix and changeover frequency. Identify physical constraints: floor space, ceiling height, and utility capacity. Document growth projections for the next 5 years. The capacity definition ensures the integrated line meets current needs and accommodates future expansion.
Step 2 — How do you calculate potential labor savings, error reduction, and quality gains?
Compare baseline labor requirements to projected staffing after integration. Real-time data exchange through integrated software improves operational efficiency and allows for quicker decision-making and adaptability to changing market demands, factors that should be quantified in ROI, labor, and quality calculations. Calculate quality improvements as reduced scrap value plus avoided customer returns.
Step 3 — How do you model throughput improvements and compare scenarios?
Calculate increased output as (new line speed - baseline speed) × operating hours. Model multiple scenarios: conservative, expected, and optimistic performance. Account for ramp-up periods when operators learn new equipment. Throughput modeling reveals whether capacity gains justify investment or if other benefits drive ROI.
Step 4 — How do you calculate payback period, ROI percentage, and NPV?
Payback period = total capital investment ÷ annual savings. ROI percentage = (total savings - total investment) ÷ total investment × 100. ROI benefits from predictive maintenance include reduced downtime and catastrophic failure prevention, which must be factored into payback period and NPV calculations. Payback periods under 3 years typically receive management approval.
Step 5 — How do you validate the model with pilot tests, vendor data, and simulations?
Request performance guarantees from equipment vendors. Visit reference installations operating similar products. Run pilot tests on vendor equipment to verify speeds and quality. Conservative projections based on validated data build confidence in the financial model and reduce implementation risk.
How do weighing and filling accuracy influence overall ROI?
Accurate dosing reduces raw material costs, improves regulatory compliance, and increases customer satisfaction. Precision filling equipment delivers faster payback through reduced giveaway and higher throughput.
How does improved accuracy reduce product giveaway and raw-material cost?
Product giveaway occurs when actual package weights exceed target weights. A 1% reduction in giveaways saves $100,000 annually for a facility producing $10 million in products. Multi-head weighers achieve ±0.5% accuracy compared to ±2% for volumetric systems. Improved accuracy allows manufacturers to target lower average weights while meeting minimum weight regulations.
How do faster filling systems contribute to line speed and reduced bottlenecks?
Filling equipment often determines maximum line speed. Servo-driven fillers achieve 20% to 40% higher speeds than pneumatic systems. Faster filling eliminates upstream bottlenecks and enables downstream equipment to operate at rated capacity. Speed improvements increase daily output without extending operating hours or adding shifts.
How does precision dosing reduce rejects, rework, and regulatory risk?
Accurate filling reduces underfilled packages that fail checkweigher verification. Consistent fill levels improve package appearance and reduce customer complaints. Precision dosing provides documented compliance with weights-and-measures regulations. Fewer rejected packages lower scrap costs and improve first-pass yield.
How do primary and secondary packaging machines shape ROI outcomes?
Packaging equipment directly impacts labor requirements, material efficiency, and production flexibility. Equipment selection determines changeover speed, format variety, and maintenance demands.
How does matching the packaging machine speed with the upstream weighers prevent bottlenecks?
Packaging machines must operate at or above filling equipment speed to prevent accumulation and line stalls. Mismatched speeds create persistent bottlenecks that limit overall throughput. Proper speed matching eliminates the need for excessive buffer conveyance between stages. Speed analysis identifies whether packaging or filling equipment limits line capacity.
How do automated film/pouch handling and changeover presets reduce downtime?
Automatic film splicing eliminates manual roll changes and production interruptions. Recipe-driven changeovers adjust machine settings electronically rather than through manual positioning. Automated systems achieve changeover times 50% to 70% faster than manual methods. Reduced downtime increases available production time and improves schedule adherence.
How do case packers and cartoners influence labor reduction and packaging consistency?
Automated case packing eliminates manual loading and reduces labor requirements by 2 to 4 operators per line. Robotic systems handle diverse package types without tooling changes. Consistent case counts improve inventory accuracy and shipping efficiency. Case packers typically provide a 2-to-4-year payback in high-volume operations.
How do inspection systems and end-of-line automation impact payback?
Quality verification and material handling automation protect product integrity and reduce labor costs. These systems deliver measurable ROI through scrap reduction and injury prevention.
How do checkweighers, metal detectors, and vision systems prevent costly quality escapes?
In-line inspection catches defects before they reach customers. Checkweighers verify correct fill weights and reject non-conforming packages. Metal detectors prevent contaminated products from entering distribution. Vision systems inspect seals, labels, and package appearance. Preventing one major recall event can justify the entire inspection system investment.
How do palletizers and stretch wrappers reduce manual labor and injury risk?
Manual palletizing requires heavy lifting and repetitive motion that causes cumulative trauma injuries. Robotic palletizers eliminate this ergonomic hazard entirely. Automated palletizing reduces end-of-line staffing from 2-3 operators to 0.5 operators per line. Labor savings from palletizing typically deliver a 2-to-3-year payback.
How does synchronous end-of-line operation eliminate downstream stalls?
Integrated control ensures palletizers receive cases at optimal rates without overloading or starving. Automatic pallet dispensing prevents delays waiting for empty pallets. Coordinated stretch wrapping maintains continuous case flow from packers. Synchronous operation maximizes end-of-line throughput and prevents cascading slowdowns across the entire line.
How do financing options and risk factors influence ROI modeling?
Financing structures affect cash flow timing and total project cost. Risk assessment identifies potential issues that could delay payback or reduce expected returns.
How do loans, leases, and phased investments change ROI timelines?
Equipment loans spread payments over 3 to 7 years, preserving working capital. Leases offer tax advantages and lower monthly payments but higher total costs. Finance charges of 5% to 8% add to the total project cost and extend payback periods by 6 to 18 months. Financing choice depends on corporate capital availability and strategic priorities.
How do ramp-up curves and learning periods affect early-stage payback?
New equipment requires operator training and process optimization before reaching rated performance. Learning periods typically span 3 to 6 months. Production rates during ramp-up average 60% to 80% of eventual capability. Conservative ROI models assume full benefits begin 6 months after startup.
How do risk scenarios alter expected ROI, NPV, and long-term savings?
Market demand changes affect the value of increased throughput. Product mix shifts impact anticipated changeover savings. Commodity price fluctuations alter raw material giveaway benefits. Scenario analysis identifies break-even points and worst-case outcomes. Conservative assumptions protect against overestimating returns and establish realistic management expectations.
How does Wolf-Packing Machine Company support full-line integration and ROI planning?
Wolf-Packing Machine Company provides complete packaging systems from initial dosing through palletizing. Their integration expertise, controls capabilities, and support services help manufacturers achieve projected ROI targets.
How does Wolf-Packing design complete lines from weighers to palletizers?
Wolf-Packing engineers design integrated systems tailored to specific products, formats, and production rates. They specify equipment from trusted suppliers and integrate components into unified systems. Complete turnkey solutions include mechanical installation, controls programming, and factory testing. Comprehensive design services eliminate coordination problems that occur when manufacturers assemble lines from multiple vendors.
How does Wolf-Packing ensure machine-to-machine synchronization through controls and communication?
Wolf-Packing programs master control systems that coordinate all line equipment. They configure PLCs, establish communication networks, and develop HMI screens. Control system design enables automatic speed matching, accumulation management, and synchronized startups. Unified control systems simplify operator training and streamline troubleshooting.
How does Wolf-Packing assist with ROI modeling, payback projections, and operational benchmarking?
Wolf-Packing provides ROI analysis tools and benchmarking data from previous installations. They help manufacturers quantify labor savings, throughput gains, and quality improvements. Performance guarantees establish accountability for projected results. Accurate ROI models set realistic expectations and measure post-installation results.
How do training, commissioning, and long-term support protect ROI after installation?
Wolf-Packing provides onsite operator training during commissioning and startup. They offer ongoing technical support via phone, remote diagnostics, and field service. Preventive maintenance programs protect equipment reliability and sustain performance. Long-term support ensures lines maintain projected performance throughout their operational life.
What KPIs confirm ROI gains after integration goes live?
Post-installation measurement validates ROI projections and identifies additional improvement opportunities. Tracking key metrics ensures benefits materialize and persist across shifts and product changes.
How should you track OEE, uptime, and throughput changes post-installation?
Calculate OEE weekly and compare to baseline measurements. Improved operational efficiency from predictive maintenance ensures equipment operates at optimal performance levels, leading to higher productivity, reduced energy consumption, and improved product quality—all measurable through OEE and throughput KPIs. Track uptime as (operating hours ÷ scheduled hours) × 100. OEE gains of 10 to 20 percentage points validate integration success.
How should you monitor labor productivity, changeover time, and scrap reduction?
Count operators required per shift and compare to baseline staffing. Measure changeover duration from the last good package to the first good package. Track rejection rates daily by rejection reason. Calculate labor productivity as (units produced ÷ labor hours). Monitor these metrics across all shifts to identify training needs or procedural inconsistencies.
How do real-time dashboards and analytics support continuous improvement?
Dashboards display current line status, production counts, and efficiency metrics. Alerts notify supervisors of downtime events requiring attention. Trend analysis reveals gradual performance degradation, indicating the need for maintenance. Data-driven insights guide continuous improvement initiatives that extend beyond initial installation.
What questions do manufacturers commonly ask about packaging line integration ROI?
Manufacturers evaluating integration projects face concerns about risk, flexibility, and implementation complexity. These common questions address practical considerations affecting investment decisions.
Can an existing facility achieve high ROI without major floor-layout changes?
Existing facilities can integrate equipment within current layouts by optimizing equipment placement and using vertical conveyance. Elevated conveyors preserve floor space while connecting machines. Phased integration allows incremental improvements without complete line replacement. Retrofit integration typically achieves 60% to 80% of the benefits available with greenfield installations.
Can phased integration deliver partial ROI before full integration is complete?
Phased approaches integrate high-impact zones first, delivering immediate returns that fund subsequent phases. Starting with end-of-line palletizing provides rapid labor savings. Adding mid-line integration eliminates material handling and improves flow. Each phase delivers measurable benefits and improves overall system performance.
Can integrated lines stay flexible enough for frequent SKUs and format shifts?
Recipe-driven equipment handles format changes quickly through automated adjustments. Quick-change tooling enables mechanical changeovers in minutes rather than hours. Vision-guided robots adapt to different case patterns automatically. Integration improves flexibility by coordinating format changes across all equipment simultaneously.
Can ROI goals be met in highly regulated or high-mix production environments?
Enhanced safety from predictive maintenance identifies potential hazards before they result in accidents or injuries, reducing the risk of equipment malfunctions that could pose safety threats—critical for meeting ROI goals in highly regulated environments. Sanitary design and automated cleaning systems address food-safety requirements while reducing cleaning time. Electronic batch records simplify regulatory compliance and audit preparation.
What should teams remember when evaluating ROI for complete packaging line integration?
Successful integration requires thorough analysis, realistic projections, and commitment to long-term performance. Strategic decisions determine whether investments deliver expected returns.
What strategic priorities should guide the final investment decision?
Define objectives and scope clearly by determining which equipment or systems will be monitored and integrated. Prioritize benefits aligned with business strategy: labor reduction, capacity expansion, or quality improvement. Deploy IoT sensors on selected equipment to collect real-time data, with sensors strategically placed to capture relevant parameters such as temperature, vibration, humidity, and pressure. Balance capital constraints against operational needs and growth projections.
What immediate next steps help teams move from early evaluation to full ROI modeling?
Temperature sensors monitor the thermal condition of machinery, motors, and critical components. Vibration sensors are crucial for identifying mechanical problems in rotating equipment like motors, pumps, and compressors. Humidity and moisture sensors monitor moisture levels that can impact equipment performance. Regular monitoring and timely maintenance interventions extend the lifespan of manufacturing equipment by addressing issues at an early stage. Predictive maintenance minimizes unplanned downtime by identifying potential issues before they escalate into major failures. Collect baseline performance data, visit reference installations, and develop preliminary ROI models using conservative assumptions.
Transform Your Packaging Line ROI into Reality
Wolf-Packing Machine Company delivers complete integration solutions—from vertical form fill and seal machine systems to end-of-line automation—that achieve measurable ROI through expert system design, proven controls architecture, and comprehensive support services. Our engineering team helps manufacturers quantify benefits, validate projections, and implement systems that deliver promised returns.
Contact Wolf-Packing today to schedule an ROI analysis and discover how integrated packaging automation can transform your operational and financial performance.